Forex Trading UK for Beginners
Forex trading is legal in the UK & is regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority. Read our guide on how you can trade forex in the UK through licensed forex & CFD brokers. Also learn about the risks of Forex Trading.
The foreign exchange (forex) market is the world’s largest capital market, where more than 6 trillion worth of USD are exchanged every day on average. It can be overwhelming for beginners to get started with forex trading.
Forex trading can be profitable but it also involves financial risk. It is better to start forex trading only after understanding the fundamentals, terminologies, and basic details associated with forex trading.
This introductory guide will tell you about the basics of forex trading along with helpful tips, risk mitigation techniques, and how to develop a trading strategy. It will also highlight the pros and cons of forex trading to ensure that you make an informed decision. Without further ado, let’s get started with the fundamentals of forex trading.
6 Steps to Start Forex Trading for Beginners in UK
Summary Table of FCA Regulated Forex Brokers in UK for Traders in 2024
| Broker Name | Highlights | Trading Fees (Benchmark EUR/USD Standard Accounts) | Account Minimum | Max. Leverage | Learn More |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
XTB Ltd is authorized by FCA under FRN (Reference No.) 522157. |
Commissions
Minimum spread of 0.6 pips
with Standard Account |
Account Minimum
0
|
Max. Leverage
1:30 for forex
|
Open Account
on XTB |
|
|
StoneX Financial Ltd. is authorized by FCA under FRN (Reference No.) 446717. |
Commissions
Minimum spread of 0.5 pips
with Standard Account |
Account Minimum
$150
|
Max. Leverage
1:30 for forex
|
Open Account
on City Index |
|
|
CMC Markets UK Plc is authorized by FCA under FRN (Reference No.) 173730. |
Commissions
Minimum spread of 0.7 pips
with Standard Account |
Account Minimum
0
|
Max. Leverage
1:30 for forex
|
Open Account
on CMC Markets |
|
|
Pepperstone Limited is authorized by FCA under FRN (Reference No.) 684312. |
Commissions
Minimum spread of 0.6 pips
with Standard Account |
Account Minimum
0
|
Max. Leverage
1:30 for forex
|
Open Account
on Pepperstone |
Chapter #1
What is Forex Market?
Forex trading is like a global market where people trade different currencies. Imagine you have two kinds of money, let’s say dollars and euros. You want to exchange some of your dollars for euros because you think the euro might become more valuable.
So, you go to this big market, and you find someone who wants to trade their euros for your dollars. You agree on a price, make the trade, and now you have euros instead of dollars. If the euro’s value goes up, you can exchange it back for more dollars and make a profit.
But it’s a bit like a game because the values of currencies keep changing all the time. So, you need to be careful and think about when to trade to make money. Forex trading is like playing with money from different countries and trying to win by trading them at the right time.
The foreign exchange market, or forex market, serves as a global platform for the exchange of currencies at prevailing rates. It facilitates international transactions by necessitating the exchange of different currencies. To ensure a fair trade, currencies are exchanged based on conversion rates, which vary for each currency pair and are influenced by a multitude of economic and geopolitical factors.
Traders engage in the forex market by analyzing these factors to predict the price movements of currency pairs. Leveraging their insights, they place buy or sell orders through margin trading. However, it’s crucial to recognize that forex trading carries a high level of risk, and many beginners face initial losses.
The forex market offers a diverse range of currency pairs, categorized as major, minor, and exotic. The EUR/USD pair is the most heavily traded globally, closely followed by GBP/USD. Trading in any currency pair signifies the exchange of one currency for another, underlining the intricate dynamics of this financial market.
Currencies are essential for global trade as they enable buying and selling commodities, products, and services locally and worldwide. It provides a means for international trade. For instance, if you’re living in the UK and want to buy an imported car from the US, you might need to pay in US dollars. That means you must convert your British Pound into US dollars to pay the bills for this purchase.
One unique characteristic of the FX market is that there is no centralized marketplace where foreign exchange can happen. It is conducted electronically via connected networks rather than on a centralized exchange as the stock trade happens. Secondly, the FX market operates 24 hours a day and five days a week in major financial centres, such as London, Tokyo, and New York. It can be traded around the clock because of time zone differences. For example, when trading sessions end in New York, it begins in Singapore and Tokyo. In sum, the forex market never sleeps.
Foreign Exchange Brief History
The history of the forex market is as old as the world’s trading history. In the beginning, people bartered goods and later used precious metals and stones to buy and sell goods and services. However, the present foreign exchange is a relatively modern phenomenon.
The modern forex history begins with the establishment of Bretton Woods in 1944, where selected currencies were pegged against the US dollars. By 1971, more currencies were included in the currency basket. Each currency derived its value based on demand and supply.
Most of the trading happens via commercial and investment banks, which trade on behalf of their clients. Retail investors also speculate on the currency values to earn a profit. They can profit via two options, either through interest rate differential or making money from changes in the exchange rate.
Investors keep shorting their currencies with lower interest rates in exchange for currencies with higher interest rates. For instance, if the US Federal Reserve increases the interest rate, those holding Japanese yen can sell their yen for US dollars.
Forex trading used to be difficult for retail investors before the internet. MNCs, hedge funds, or high-net-worth individuals were the leading players as currency trading required significant capital. However, things started to change around the 1990s as the internet made it easy for individual traders, as brokers and banks provided access to electronic trading. Today, online brokers enable retail investors to place a trading order with a very minimum amount known as leverage.
3 ways to trade forex
There are three main ways to trade in foreign exchange: spot, forward, and future.
Spot market
The spot market is also known as the ‘cash market,’ where currencies are bought and sold and delivered on the spot. The price of a currency in the spot market is determined by demand and supply. That means the more the demand for a currency higher the value of that currency.
However, it’s not that simple. Some countries intentionally keep the currency values low to make export cheaper or attract foreign investments. The currency value is calculated on many factors, such as interest rate, market sentiment, political change, and economic news.
The final deal between one party that sells an agreed-upon currency price and the other that buys that agreed-upon exchange rate is known as a ‘spot deal.’ Once you close the position, you receive the specified amount of that currency in cash. Although the spot deal is considered spontaneous, the cash settlement usually takes two days.
Forward market
A private agreement between the two parties to buy a currency at a future date and the pre-agreed price is a forward contract. Let’s take an example to understand how a forward contract works.
Assume that a UK car company wants to secure a contract for a future purchase of spare parts from X, which is located in the US. The UK company signs an agreement with the US company to buy the spare parts after six months.
Both agree for a future exchange rate of 1 GBP = 1.3700 USD, and at the time of the agreement, 1 GBP is equal to USD 1.3700. Now suppose, after six months, the value of one dollar drops to 1.3800. That means the importer will benefit by USD 0.01 per unit of the exchanged currency. Now reverse the situation, the price of one dollar increases to 1.36.
In this case, company X (exporter) will benefit from the forward contract to hedge their risk. The vital thing to note is that currency value can move in any direction, either up or down. Who benefits from a forward contract depends upon the value of one currency against the other after six months.
Future market
A future agreement is similar to a forward contract; the only difference is that the latter is a standardized contract. The futures contract is a standard contract that specifies the quantity of a particular asset at a pre-determined price and delivery date.
For example, suppose Indian Oil signs a future contract to import 1 million barrels of oil with an oil producer based in Saudi Arabia. The oil producer promises to deliver the specified quantity in twelve months at a pre-agreed price of $75 per barrel.
So even when the price of one barrel falls to $70, the importer is obligated to pay the premium. The same is true when the price reaches $80; the oil producer will deliver the quantity despite the changes in the spot price.
Chapter #2
What is Forex Trading?
You must have exchanged your national currency with a foreign currency if you have visited abroad. It is the simplest example of how forex trading occurs. In forex trading, you buy one currency and sell another while the exchange rate fluctuates based on several factors, but mostly supply and demand.
A significant portion of trades in the forex market occurs between financial institutions. These institutional traders such as investment bankers, wealth managers, and others speculate or hedge against deviations from future exchange rates.
For instance, a fund manager can exchange euros for dollars if he thinks the dollars will strengthen in the coming days. On the other hand, a European company can hedge against price fluctuations in the event if the Euro weakens.
How are currencies traded on the exchange?
All currencies are represented with a three-letter symbol—Euro as EUR and American dollar as USD. Forex trading always involves a currency pair, such as EUR/USD or USD/GBP.
The most traded currency pairs accounting for 75% of total forex volume are:
- Euro/US Dollars (EUR/USD)
- USD/ Japanese Yen (USD/JPY)
- Great Britain Pound/USD (GBP/USD)
- Australian Dollar/USD (AUD/USD)
- Canadian Dollar/USD (CAD/USD)
- Swiss Currency/USD (CHF/USD)
- New Zealand Dollar/USD (NZD/USD)
As you can see, every major currency pair involves the US dollar; that is the reason why American dollars are called ‘Global Currency’. The US dollars account for roughly 88% of the global trade payment as per BIS Report in April 2019.
How are Currencies Quoted?
Let’s take an example to understand how currency pairs are quoted in forex trading. You can apply this understanding to every currency pair. We will take USD/GBP for our example.
- On the left is the base currency (USD) and the quote currency (GBP) is on the right.
- The base currency is always expressed as one unit, while the quote currency varies depending on its value for a unit of the base currency. In the USD/GBP example, the exchange rate tells you how much the British Pound will require to buy one American dollar unit.
- If the current exchange rate of USD/GBP is 0.71, that means 0.71 GBP can be exchanged for 1 USD. Generally, the Pound is quoted as GBP/USD, so at the exchange rate of 1.36, you can exchange 1 British Pound for 1.36 US Dollar.
- • If the exchange rate rises, that means the value of the base currency has increased. In contrast, when the exchange rate falls, that means the value of the quoted currency has increased. For example, if the GBP/USD rises to 1.40, it means that the British Pound has become more valuable compared to the US Dollar.
Standard Forex Terms to Know Before Trading
1. Currency Pair:
As shown in the above example, forex trading always involves two currencies. Generally, the currency pairs are divided into three categories: major, minor, and exotic.
A currency pair comprises two currencies namely the base currency and the quote currency. The currency that the traders intend to buy or sell is called base currency while the currency that is exchanged in return for base currency is called quote currency. In EUR/USD currency pair, EUR is the base currency and USD is the quote currency.
There are seven major currency pairs, including EUR/USD and USD/JPY. EUR/USD is the most traded currency pair globally.
Those currency pairs that don’t involve US dollars are known as minor pairs. For example, EUR/GBP, EUR/AUD, and GBP/JPY are some of the most traded minor currency pairs in forex trading. The Japanese yen, Euro, and British Pound hold the most significant chunk of minor pair trading.
Lastly, when a major currency is paired with a currency from a developing country, it is called exotic currency pair. Examples are EUR/Turkish Lira, USD/Hong Kong Dollars, and others. If you’re new to forex trading, stick with major and minor currency pairs.
2. Pip (Percentage-in-point):
Pip is the standard measurement of changes in the value of a currency pair. This is the most basic mathematical measure you must understand before trading. A pip represents the last decimal of the quote currency. By convention, every quote currency is expressed as four decimal points. However, there are exceptions like JPY which is quoted with just two decimals.
For example, if the value of 1 EUR changes from 1.3455 to 1.3456 USD, that means one pip change in the currency pair. A pip is the smallest possible change in the price of a currency pair.
3. Bid-ask Spread:
The difference between the buying and selling price of a currency offered by a dealer is called the bid-ask spread or simply a spread. The bid is the price a broker is willing to pay for a currency, while the asking price represents the broker’s maximum selling price of the same currency. Wider spreads mean higher profits for the broker and lesser gains for the traders. Spreads are commonly represented in pips.
Suppose EUR/USD is trading at 1.2100/1.2102. In this example the spread or the difference between the bid and ask price of the EUR/USD currency pair is $0.0002 or 2 pips. This means that on every unit of EUR traded in return for USD, the broker or the liquidity provider will earn a revenue of $o.0002.
The spreads are variable and depend on liquidity and market conditions. However, some brokers may offer fixed spreads. Each forex pair can have different spreads at different times of the day. Traders should look out for regulated brokers that offer low or narrow spreads.
4. Lot:
Currency pairs are always traded in lots. In forex trading, one Standard lot equals 100,000 units of a currency. Additionally, there are also Micro Lot – 1000 units and Mini – 10,000 units of lot sizes.
If you are trading 10 Standard Lot, it means that you are trading 1,000,000 units of the currency. Similarly, if you are trading 5 Mini Lots, you are trading 50,000 units of a currency.
5. Leverage:
Leverage enables you to trade in large volumes with minimal marginal money. In simple terms, a forex broker provides a certain amount of money if you fulfil the initial margin requirement. For instance, if a dealer offers 10:1 leverage, you can trade ten times each deposited dollar in your trading account. Forex traders use leverage to place large orders and profit from small price changes in a currency pair.
For example, if you intend to place a trading order for one standard lot of USD/EUR using the 10:1 leverage. That means if you deposit $1000 in your trading account, you can open trading positions worth $10,000. Beginners should tread the leverage water very carefully because it can amplify both profits and losses. That’s why experts call leverage a double-edged sword.
It must be noted that the majority of retail forex traders lose money. All the FCA-regulated forex brokers are required to mention on their website the exact percentage of retail traders who lose money with that broker while trading CFDs.
6. Margin:
The amount you put in your trading account to use leverage is called margin. Suppose if your broker offers a leverage of 1:10, you need to have $1 in your account to open a position worth $10 at a given leverage ratio.
7. Long/Short:
Forex trading allows clients to make profits or losses on bullish as well as bearish market trends. Going long means traders will earn a profit when the price of quote currency increases while short means profit on bearish trends.
Suppose a long and short position on EUR/USD is opened at 1.2000. Traders with a long (short) position will earn a profit if the price of 1 EUR moves above (below) $1.2000 USD.
Market Trading Terms
Some terminologies are based on market activities and traders must acknowledge these to understand price movements in the forex market.
1. Bull Market
Bullish trend or bullish market is a commonly used term in financial markets to denote appreciation in the price of the asset. For example, a continuous rise in prices of a commodity or stock for a prolonged period will be called a bullish trend.
In a forex pair, a bullish trend can be due to appreciation as well as the depreciation of one currency with respect to other. For example, a bullish trend in EUR/USD currency pair represents an appreciation of EUR and/or depreciation of USD.
2. Bear Market
A bearish trend or bearish market is exactly the opposite of a bullish trend. Continuous depreciation in the price of an asset is commonly denoted as a bearish trend.
In the forex market, appreciation of quote currency and/or depreciation of base currency can be called a bearish trend on a currency pair.
3. GDP
GDP or Gross Domestic Product is the total value of all the goods and services produced in a country in a particular time period. It is a popular indicator that represents the overall health of a nation’s economy.
Growth in GDP can be compared with other nations to predict the increase or decrease in the price of a currency pair. For example, in a hypothetical currency pair ABC/XYZ, the GDP of the country with ABC currency increases more than the GDP of XYZ nation. This means ABC is growing faster than XYZ and the price of ABC in terms of XYZ is very likely to increase.
4. Inflation
Inflation means a rise in prices in a nation over a time period. There are multiple factors in an economy that can increase or reduce inflation. Each country has different inflation rates at a particular time interval.
Inflation rates of two currencies involved in a currency pair can be compared to predict the price movement of a currency pair. The country with a higher rate of inflation will lose its value against the one that has a lower inflation rate.
5. Interest Rates
The interest rate of a country that is also known as the repo rate is the basic rate at which the central bank will provide loans in a particular nation to commercial banks. Interest rates also depict the rate at which investors can earn through fixed deposits in the country.
Interest rates are decided by the central bank or the monetary authority of a nation. Interest rates can be comprehended to predict the price movements in a currency pair.
Latest Development and Technological advancement in Forex Trading
The latest developments and technological trends in Forex trading with the use of AI as of 2024 are quite groundbreaking. Here’s an overview of the key advancements:
Automated Trading Systems and AI Traders: AI-driven automated trading systems have become more prevalent, accounting for a significant portion of forex transactions. These systems are capable of analyzing large datasets rapidly, identifying market trends and executing trades with remarkable speed and efficiency. This has led to the emergence of autonomous AI traders, which can react to market changes and news events almost instantaneously, providing an edge over traditional human traders.
AI-Driven Market Sentiment Analysis: The use of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms in sentiment analysis has become a critical tool. By analyzing news articles, social media, and online content, AI can gauge public sentiment towards different currencies, offering traders valuable insights for making more informed decisions.
Virtual and Augmented Reality in Trading: The integration of AI with Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies is reshaping the trading experience. This includes immersive environments with interactive forex data visualizations, AI-generated alerts in AR overlays, realistic forex training simulations, and collaboration in virtual spaces.
Real-Time Big Data Processing: The ability to process and analyze large datasets in real-time has become crucial. Big Data technologies enable traders to stay updated with the latest market movements and news, allowing them to make quicker and more informed decisions.
Hyper-Accurate Forex Analysis and Predictive Analytics: Advanced machine learning techniques are transforming forex analysis, making it possible to predict price movements with higher accuracy. Predictive analytics using historical data and statistical algorithms are providing traders the ability to anticipate market trends and currency fluctuations more accurately.
Democratized Access for Retail Traders: AI and Big Data are leveling the playing field for retail traders by providing access to advanced analytics and trading signals. Online forex brokers are offering AI tools that can analyze charts, market news, and identify trading opportunities.
Automated Risk Management: AI systems are capable of conducting rapid automated risk analyses, including real-time evaluation of risk exposures and volatility modeling. This enhances safer trading practices.
Increased Transparency and Regulation: With the rise of AI and automation, forex markets are facing stricter regulations for transparency and control over autonomous systems.
Personalized Trading Experience: AI algorithms are enabling a more personalized trading experience by learning from each trader’s behavior and preferences, offering tailored trading advice and strategies.
Growth of Social Copy Trading: Social trading platforms are being enhanced by AI, enabling smarter trader selection, dynamic copy trading, and predictive analytics for better trade filtering.
Always-Learning Algorithms: Self-improving AI algorithms are on the horizon, which will continually adapt and optimize trading strategies, making real-time adjustments to market changes.
These advancements are transforming the Forex trading landscape, making it more efficient, accurate, and accessible. The integration of AI in Forex trading is not just enhancing existing methodologies but also creating new opportunities and paradigms for traders at all levels.
Chapter #3
Understanding Forex Trading with an Example
Understanding forex trading can be complex for those who have never traded on any financial instrument online in the past. Those who have a slight experience of trading other capital markets like stocks, cryptocurrencies, or CFDs would be very comfortable with forex trading.
Let us understand the complete process and working methodology of the forex market with the help of an example.
Online forex trading is done through the trading platform which is software that can be downloaded on electronic devices. The trading platform connects traders to brokers, liquidity providers, and other forex traders.
Traders place buy or sell orders through trading platforms on their preferred trading instruments. The exposure and profit/loss depends on the volume traded and the leverage involved.
A leverage of 1:10 will allow you to open a position worth $100 exposure with $10 in your trading account.
In this example, we will take the leverage of 1:10 on the EUR/USD currency pair. The supposed market price for EUR/USD is 1.2100/1.2102. This means that the bid price is 1.2100 (the price that the dealer is willing to pay) and the ask price is 1.2102 (the price at which the dealer is willing to buy) and the spread is 2 pips (difference between the bid and ask price at 4th decimal).
First, we will place a buy order for 1 standard lot (100,000 units of the base currency). To place a buy order of 1 standard lot in EUR/USD, the following will be the calculation of the required account balance.
$1.2102 * 100,000 * 1/10 = $12,102
(ask price) * (units of base currency) * (leverage ratio) = (minimum account balance required to open the given position)
Now suppose the price of EUR/USD went up by 100 pips and reached 1.2200/1.2202. By closing the buy position at this price, the following will be the profit.
(1.2200 * 100,000 * 1/10) – $12,102 = $12,200 – $12,102 = $98
(bid price * units of base currency * leverage ratio) – (exposure) = Profit/Loss
Now let us understand the same scenario with a short position on EUR/USD with 1 standard lot at the current market price of 1.2100/1.2102. Following will be the exposure amount in a short position.
$1.2100 * 100,000 * 1/10 = $12,100
(bid price) * (units of base currency) * (leverage ratio) = (minimum account balance required to open the given position)
Now suppose the price of EUR/USD went down by 150 pips and reached 1.1950/1.1952. By closing the position at this position, the following will be the profit.
$12,100 – $(1.1952 * 100,000 * 1/10) = $12,100 – $11,952 = $148
exposure – (ask price * units of base currency * leverage ratio) = profit
It must be noted the exposure amount ($12,102 in the long position example and $12,100 in the short position example) will be at risk of capital markets. If the leverage is high, the profit/loss amount will move more with the change in the pip value of the underlying asset. Chapter #4 Now that you know about the basics of forex trading, we will delve into how to get started with forex trading. Before you place your first order, follow these steps: Anything you learn requires knowing a little about the subject. The same is true about currency trading. Beginners may be tempted to start trading with anything that moves. Using leverage unwisely and random trading is the two trading traits you must avoid. Spend time educating yourself about the currencies you are going to trade. Understanding the currency pairs can have a significant impact on your earnings. For example, the Japanese currency is moving upwards after a large fall. Or, a currency is falling rapidly due to bad economic reports over the months. These are typical examples of how underlying causes can cause currency movements.
To better understand, pick just a few major currency pairs and see how they perform over a few days. Meanwhile, keep an eye on the financial news for the countries involved. You can develop a good sense of currency movements. A trading platform enables you to place trading orders, track their performance, and monitor your trading account offered by a broker. Each trading software has different qualities suitable for the individual trading style and level of expertise. Here are the three most popular software: It is compatible with various operating systems, including Windows, Android, Mac, and Linux. It also offers a demo account for new traders and supports automated trading. Users can customize its API to create their unique strategies. It is perhaps the best all-in-all software that allows trading in forex, stocks, and futures. Beginners can start with MT5 mobile, which is free and suitable for most new traders. However, the desktop software is much better in terms of features and effectiveness.
However, it has a friendly interface. Anyone can learn to trade within one or two days. The integrated platform enhances the trading experience by combining mobile trading, trading signals, and market analysis. MT4 Mobile is ideal for new traders as it provides a multilingual interface, newsfeed, and technical analysis and is compatible with Android and iPhone. Every successful athlete spends more time in training than participating in a competition. Similarly, if you want to be a successful trader, you need to practice your strategies before risking your money. Many brokers offer a demo account to let you familiarize yourself with the ins and outs of their trading platform. The best part is that you don’t have to put any real money in your trading account. It would help if you continued trading with a demo account until you develop an excellent winning strategy and become comfortable with the platform. You don’t want to put your hard-earned money with an unscrupulous broker. Choose a forex dealer who is regulated by a trusted authority. It’s ideal if your national regulator regulates the broker; if not, choose a currency dealer with Tier I and Tier licenses from ASIC, FCA, or CySEC. For traders based in the UK, you must only trade with forex brokers that are licensed by Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). You can search for the broker’s license no. i.e. the ‘Firm Reference Number’ (FRN) on the FCA’s public search page. On the page, you can search the brokers by their Entity Name or their Reference Number. The FRN number of the registered brokers is generally mentioned in the footnote of their official website. If you cannot find it, you can ask for the regulation details through customer support services. For ex. XTB has a firm name of XTB Limited & Reference Number is 522157. You first need to make sure that you ask the broker for their FCA Reference Number. Once you have that, you can then search if that broker is actually licensed or not from FCA’s search. Everything the broker is authorised to do in the UK can be checked through the FCA website. Another important thing to note is that brokers may falsely claim to be licensed while they are not. They may target clients of genuine brokers by using their license numbers as their own. So, it is really important to check the ‘ Authorized Website’ of the broker for the public search & avoid the clones of fake brokers. After ensuring the safety and FCA regulation of the brokers, clients must check and compare the fees and other trading conditions that can affect the trading experience. The chosen broker must accept preferred deposit and withdrawal methods and offer good support services. The trading platforms and available instruments must also be checked before opening the account. Traders must do their own research to choose the best-suited brokers for themselves. Reviews from experts and existing clients can be useful but the final decision should be based on your convenience, preference, trust, and user-friendliness. Please make yourself aware of trading software and how they function. The trading platform is where traders spend most of their time and they must be comfortable with the trading platform. MetaTrader and cTrader are the most commonly chosen forex trading platforms but some brokers offer their proprietary trading platforms. The most common trading tools you should know are: Contract for differences (CFD) is a derivative instrument that is widely used in online trading of financial instruments. Most of the retail forex trading with leverage are done in the spot market as CFD. Forex, commodities, energies, metals, indices, stocks, cryptocurrencies, etc are commonly traded through CFD. When trading via CFD, only the price difference between the opening and closing of the position is speculated to book profits. There is no physical buying and selling of the underlying assets. Most of the brokers that offer online forex trading in the UK use CFD for forex trading. The account opening process at every FCA-regulated broker is nearly similar. However, the process and time required to open the live account can vary from broker to broker. Following are the steps to open a live trading account in the UK. Step 1: Select a Broker Traders must check and compare every aspect of the broker and choose the most suitable broker with regulations, low fees, availability of desired instruments, helpful customer support service, convenient deposit and withdrawals, and a user-friendly trading platform. Step 2: Visit their Website or Download the App After choosing the broker, you need to visit their official website or download the application to open the account. Step 3: Enter Basic Details The first signup process involves providing basic details like name, phone number, email, and country of residence. Some brokers may ask for a few more details. Step 4: Select Account Type Most forex and CFD brokers offer more than one account type with different pricing structures, trading platforms, or trading conditions. Traders must choose the most suitable account type while opening their accounts. Step 5: Document Verification After configuring the account and answering a few basic questions related to forex trading, traders are required to verify their documents by uploading soft copies. Brokers will ask for name and address proof which can be done with a passport, national identification document, etc. Each broker can take different times to verify the document ranging from 2 hours to 24 hours on business days. Step 6: Deposit Funds Once the account has been verified, clients can deposit funds through the accepted methods from the website or application of the broker. It is important to check the associated fees and time required to process the transaction. Step 7: Download the Trading Platform and Start Trading Once the deposits are visible in the account equity, you can open trading positions on available instruments through the trading platform. The trading platform can be downloaded on mobile and desktop devices and can also be accessed through the web. Chapter #5 Trading without strategy is like sailing without a compass. The sailor has no idea about the wind speed or the direction. That’s why the practice of forex analysis plays a vital role in currency trading. You look at the changes in the values of currency pairs and the forces that are influencing those price movements. Traders use both fundamental and technical analysis for creating a profitable strategy. Many expert traders combine both techniques to take a hybrid approach. In short, the knowledge of technical analysis will tell you when (to buy or sell) and fundamental analysis tells you why (the price movements). Both are indispensable weapons for a successful forex trader. Let’s deconstruct both methods one by one. What economic factors will impact the demand and supply of a currency? Welcome to Macroeconomics 101, the law of demand and supply. If the demand for a currency is increasing, the trader may assume the prices will rise. On the other hand, a demand reduction may be an indication of an eventual fall. However, it’s not that simple! There are many factors such as economic health, political stability, global events, and others that influence the expansion and contraction of a particular currency. For instance, the US Sub-Prime Lending Crisis in 2008 caused a massive breakdown of financial systems worldwide. The fundamental analysis generally involves the following economic indicators: In addition to global economic events, the localized changes in a national economy can also influence the currency prices of that country. For instance, the increased commodity prices globally can strengthen the Canadian dollars. Although government changes are not a frequent affair, currency prices can be affected during a transition period. The developed countries have relatively stable regimes in comparison to developing countries. Political instability is the main reason why the currencies of many African countries are so unpredictable. Central banks use monetary policy as an effective tool to control the demand and supply of a currency. They can reduce the interest rate in an economic slowdown and can increase to curb the inflation caused by economic growth. The fiscal policy entails taxation and government spending. Higher taxes can drive slower credit and economic development. Both government policies can have a significant impact on the national currency. Main participants such as banks, financial institutions, or hedge funds may buy or sell a specific currency to up or down the prices. You will be in much better positions if you have an idea about the main speculators of the forex market. Main participants such as banks, financial institutions, or hedge funds may buy or World governments publish statistical data and reports that reveal the economic health and performance over a period. Many financial reports like employment data, inflation rate, GDP, and foreign exchange reserve can indicate regional economic conditions, which can dramatically impact the local currency. A forex dealer can use an economic calendar to avoid unwanted surprises from the release of new data. Charts and graphs are the primary tools of technical analysis. Charts help traders identify historical performance, ongoing trends, and price movements and calculate risk to maximize gains from currency trading. Understanding different charting formats such as line, bar chart, and candlestick is essential to develop a solid trading strategy for beginners. The following are important terminologies associated with technical analysis. It is the most basic charting which helps users select a currency and its performance for a fixed period. The bar chart shows the highest and lowest currency price points and average performance over the period chosen. It also displays the same information: open, low, high, and close. However, the representation of data is very different from the bar chart. It becomes easier for users to see the highest and lowest peaks of the currency movements with thin vertical lines. Trend is a term used in technical analysis of capital markets that depicts the direction of the price. Generally, the price of the underlying instrument moves in a particular direction until a trend reversal is witnessed. The tops and bottoms of the charts can be analysed to identify the price trend at a given time. Trendlines and trend reversal are very important components of technical analysis. A higher-high price action followed by a higher low represents an uptrend (bullish) while a lower low and lower high depict a downtrend in price movement. Support and resistance are the prices at which the trends are likely to reverse or stop moving further in that direction. There can be multiple support and resistance levels for a single financial instrument. Support is the lower limit at which the price trend is likely to reverse or stop moving further below. Resistance is the upper limit on the price trend. Whenever a resistance or support level is broken, the price moves significantly. These limits are created due to trend reversals and stagnancy of prices in the price at that same particular level. A support or resistance level gets stronger every time it resists the price movement. As the name suggests, the moving average is an important indicator that depicts the average price movement in a given time. A moving average indicator creates a series of averages of different subsets of the full data sets of prices in a particular time interval. Current prices below the moving average depict a buying opportunity while the prices above the moving average may benefit the sellers. Fibonacci retracement levels are based on the Fibonacci sequence and are used to identify potential support and resistance levels. Traders use these levels to determine potential price retracement areas during a trend. Bollinger Bands consist of a moving average (typically 20-day SMA) and two standard deviations above and below the moving average. They help traders identify periods of high or low volatility and potential price breakouts. Candlestick charts display price data in a visual format using candlestick patterns. Traders analyze patterns such as doji, engulfing patterns, and hammers to identify potential trend reversals or continuation. Volume analysis examines trading volume accompanying price movements. It helps traders understand the strength or weakness of a price trend and identify potential reversals or breakouts. Chart patterns, such as head and shoulders, double tops, and triangles, are formed by price movements and can indicate potential trend reversals or continuations. There are hundreds of strategies that are used in the technical analysis of financial instruments. Technical analysis works well on instruments with high liquidity like the forex market. Experienced traders often use technical analysis in combination with fundamental analysis to understand why the value of a currency rises or falls for the selected period. For example, if the fundamentals indicate that the US Dollar will strengthen against the Euro due to policy divergence, and the technical analysis also indicates the same, then it is much more likely that your strategy may be successful as compared to incomplete research. You can use simple mathematical tools such as moving averages, trend lines, and others for technical analysis. You can learn about more advanced concepts like Elliott Wave Theory, Fibonacci Studies, and Pivot Points as you progress.
How To Trade Forex?
1. Learn about the currencies you want to trade
2. Get familiar with trading platforms/software
Every trading software comes with basic features like real-time quotes, charting tools, and others. Some premium software may offer a tailored trading solution for customers. The ideal platform will offer efficiency, confidentiality, and timely execution.
3. Start with a demo account
4. Choose a trusted broker

5. Understand the essential forex tools
6. Difference Between CFD and Forex Trading
Steps to Open a Forex Trading Account in the UK
Forex Trading Strategies
Fundamental Analysis
1. Economy:
2. Political Changes:
3. Monetary and Fiscal Policy:
4. Activities of Major Participants:
5. Economic data and reports:
Technical Analysis
1. Bar chart:
2. Candlestick:
3. Price Trends:
4. Support and Resistance
5. Moving Average
6. Fibonacci Retracement
7. Bollinger Bands
8. Candlestick Patterns
9. Volume Analysis
10. Chart Patterns
Chapter #6
Forex Trading Risks
Retail Traders choose to trade in currencies for profit. But almost 70% of them lose money trading forex & CFDs. How so? Well, there are plenty of reasons, from dealing with unreliable brokers to unwise use of leverage (trading with very high leverage). Beginners are advised to heed caution when they start currency trading.
Forex market works around the 24-hour clock, but it doesn’t mean you should trade the whole day. There are only a few peak hours, which are considered worth trading. With competition from market makers and large financial institutions with their trained workforce and advanced automated Trading Bots, beginners can get overwhelmed when the price movements don’t confer with their prediction. Another risk factor is leverage. Brokers give you very high leverage on your initial margin money, but that doesn’t mean you should use it every time.
Here are the Major Risk Elements of Forex Trading
1. Unregulated Broker Risk:
Online forex trading has attracted thousands of retail investors in the UJ. Trading with a trusted and well-regulated broker ensures your funds are in safe hands. If something goes wrong, there is a security mechanism that comes into play to protect your investments.
National, as well as major Tier-1 Forex Broker regulators, ensure that brokers offer fair and transparent trading environments. They set standard criteria and reporting requirements for a forex dealer before providing services to its clients. They also continue to monitor the broker’s trading practices and in case of wrongdoing, the financial regulator can cancel the broker’s license.
Before choosing, ensure that your broker is well-regulated and trusted. Don’t get persuaded by Pyramid schemes offering unbelievable returns. There are plenty of examples of when retail investors lost their money.
The best way to avoid this risk is by selecting a broker having Tier I or Tier II licenses. Tier I indicates the highest level of trust, and Tier II has a low level of confidence. UK, European, American, Australian, and Canadian regulators score well on their trust level and are called Tier I regulators. On the other hand, CySEC is considered a Tier II regulator.
Traders based in the UK must only trade with forex brokers that are regulated by FCA. You must check the products for which the forex broker/firm has been Authorised, and verify the Firm’s Reference No. and their website from FCA’s Register. Only this will ensure that you are trading with an authorized firm.
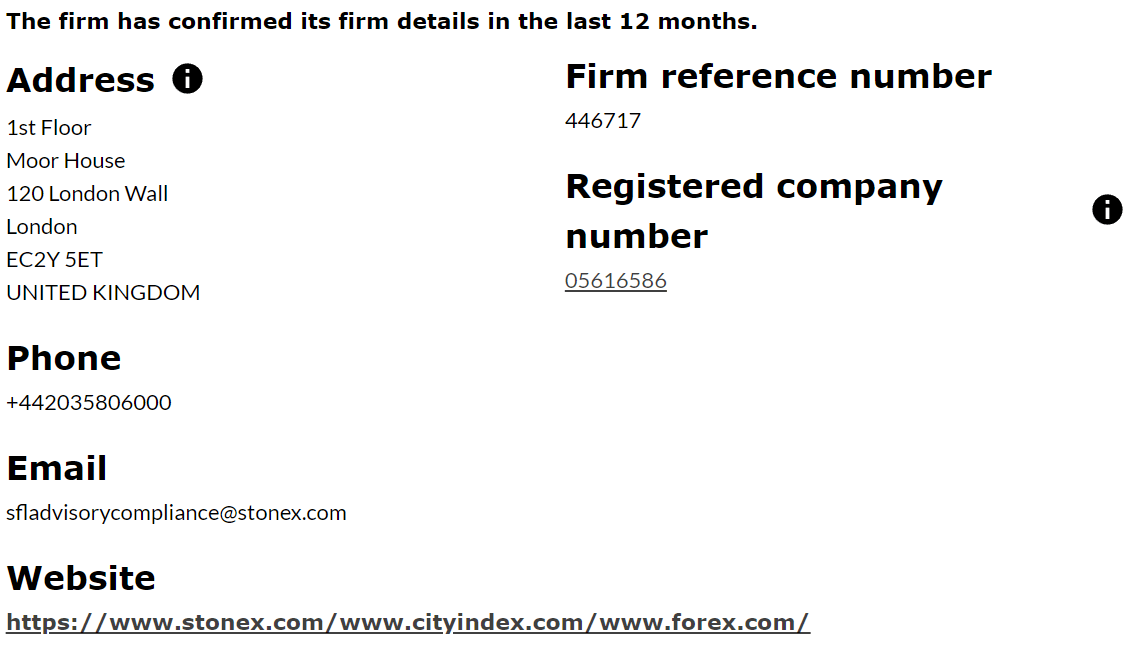
Below is an example of a City Index CFD broker that is licensed with the FCA with FRN 446717.
| Tier I & II Regulators Country Global Services | Country | Tier I & II Regulators Country Global Services |
|---|---|---|
| FCA | United Kingdom | Europe & other regions |
| BaFin | Germany | Europe |
| CySEC | Cyprus | Europe & other regions |
| ASIC | Australia | Australia and Asia |
| FSCA | South Africa | Africa |
| CMA | Kenya | Kenya |
For UK Based traders, you must only trade via a FCA regulated forex broker. If your country lacks a local regulation, choose a broker with a license from these Tier I or Tier II regulators. It is best if the forex broker/dealer has multiple regulatory permits i.e. it is licensed under multiple Top-tier regulations.
2. High leverage risk
Leverage is the same as you borrowing money from a bank which ultimately needs to be repaid. Let’s take an example of how leverage can pose a risk for beginners.
Suppose your broker offers a 1:10 leverage, which means you can place a trading order worth USD 10,000 by depositing USD 1000 as margin money in your trading account if you use leverage to place an order on EUR/USD when 1 EUR is equal to 1.1100 USD. The market gains by 100 pips, and it changes to 1.1200 USD; you profited 10% or USD 100 on your invested capital. But if the trade doesn’t go in your favor, and the market dips by USD 1.1000, you lose USD 100 or 10% of initial capital.
In sum, there is a possibility of significant profit with low capital, but there is also an equal chance of losing. Profit is possible in forex trading but not guaranteed. Beginners should begin with no leverage or a maximum 1:3 leverage ratio. Once you become experienced in having solid risk management, you can opt for higher leverage.
It is a fact that most Retail traders lose money while trading CFDs. So, it is really important that you avoid the use of leverage or not use more than 1:3 leverage for trading forex. In the UK, FCA-regulated Forex brokers offer max. leverage of 1:30 for trading forex, and leverage is lower for other CFD instruments.
3. Volatility risk
Any significant political, social, financial, or natural disaster news can impact the currency within a country. The forex market is very volatile, and every major event happening around you can influence currency trade. Market sentiments can also cause movements in a currency pair. For instance, if too many traders start to convert US dollars into Japanese Yen, the former’s value would fall.
Staying updated with current events is the only way to avoid volatility risks. Act fast during volatile currency price movements. However, know that unforeseen circumstances such as COVID-19 or the end of Swiss France capping may still cause changes in the foreign exchange. During these events, withdraw your money quickly to prevent further losses.
4. Interest rate
It’s a simple macroeconomic concept—the higher the interest rate, the higher the investment in a country.
A country’s interest rate influences the exchange rate of its national currency. When the central bank increases the interest rate, investment increases; on the other hand, a falling interest rate can cause disinvestment and lower currency value. Forex traders are expected to pay close attention to the intricate relationship between the currency and interest rate before opening or closing a trading order.
5. Country risk
Global investors and companies often access a country’s fundamentals before investing their capital. Some countries, mainly developed ones, have a stable government and are relatively stable. USA, Western Europe, Japan, Australia, and a few other countries are considered safe for foreign investments. On the other hand, political instabilities in some countries often result in unpredictable currency inflation or deflation. Nobody wants to invest in a country where the value of the currency is volatile.
Similarly, if your investments are in an unstable country’s currency, you may lose money. It happens because investors lose confidence in the economy and start withdrawing their capital. Taking clues from prominent investors, even traders sell out their currency investments.
Some countries deliberately devalue their currencies to increase exports. It poses a risk for your forex investments in that country. That’s why trade experts advise investing in major currency pairs and avoiding exotic pairs.
5. Connectivity and Technical Glitch
Forex CFD trading is done online through trading platforms on electronic devices. The devices used for trading need an active internet connection without lags and glitches. The network must be safe from hacks and external attacks.
The device used for trading must be in good condition. Any lags or hanging of the device may lead to missing out on the trading opportunities. The use of public wifi should be avoided for trading. The passwords and login credentials should not be compromised.
There are multiple risk elements in the forex market. Choosing the right broker, taking informed decisions, technical and fundamental analysis, and other precautionary measures will reduce the risk factor. However, risk in the forex market can be mitigated but cannot be removed completely.
Leveraged forex trading involves significant financial risk. Forex trading is easily accessible for retail traders. More than 70% of forex traders face losses. It is always advisable to use the demo account and trade with virtual currencies before trading with real money. This will also allow traders to know whether forex trading is suitable for them or not.
To mitigate these risks, forex traders should:
- Educate themselves about the forex market and trading strategies.
- Use risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders and position sizing.
- Avoid excessive leverage and only trade with capital that they can afford to lose.
- Stay updated on economic events and news that may impact the forex market.
- Remain disciplined and avoid making emotional decisions based on short-term market movements.
Risk management techniques in forex trading
Position Size: Determine trade size based on account balance and risk tolerance (1-2% per trade).
Stop-Loss: Set stop-loss orders to limit losses if the market moves against you.
Take-Profit: Use take-profit orders to secure gains at a predefined level.
Risk-Reward Ratio: Aim for favorable risk-reward ratios (1:2 or better).
Diversification: Spread risk by trading different assets, not all in one.
Control Leverage: Use leverage carefully to align with risk tolerance.
Trading Plan: Develop a clear plan with entry/exit rules and risk limits.
Emotions: Manage emotions to avoid impulsive decisions.
Stay Informed: Be aware of market events that could impact trades.
Monitor Trades: Adjust stop-loss and take-profit levels as needed.
Review Trades: Analyze trades to learn and improve strategies.
Avoid Revenge Trading: Don’t trade impulsively to recover losses.
Forex trading can be rewarding, but it is crucial to approach it with a clear understanding of the risks involved and to trade responsibly. Traders should consider seeking advice from financial professionals and only trade with money they can afford to lose.
Chapter #7
Pros and Cons of Forex Trading
There are some pros for traders trading in the forex market over other financial markets. But you must understand all the risks before making a decision whether to trade forex & CFDs or not..
Pros of Forex Trading
Following are the advantages of trading forex:
Largest Capital Market
You invest in the world’s largest financial market. With daily transactions crossing over USD 5 trillion, the sheer size of the forex market makes it truly a global marketplace with several profit opportunities.
24-Hour Market
The forex market operates around the clock so that you will find a trading opportunity any time of the day in at least one global time zone. As the forex market is a decentralized OTC market, its working hours are not subject to any centralized exchange system. For instance, trading hours begin at 5 PM EST in the USA on Sunday and rolls continuously with other markets until Friday at 5 PM. Note that even though currency trading is restricted for retail traders on weekends, the exchange rate keeps moving.
Low Capital Requirement and Lower Transaction cost
In addition to very low investment requirements, even the transaction cost of trading forex is relatively lower. For instance, you can start dealing in currencies with just USD 100 or even lower. The main earning of a broker comes from the bid-ask spread. Spread is measured in pips, the difference between the sell and buy price of a currency. However, some brokers do charge a commission or flat fees per transaction. You should factor in commission and spread while choosing a broker to lower your overall trading cost.
Availability of Leverage
The availability of high leverage is perhaps the main reason why forex trading appeals to so many people. It enables you to place a higher trading order with minimum capital.
Almost all the forex brokers offer leverage where you can borrow against deposited money in your trading account. It’s similar to taking a mortgage against your property; the only difference is that the margin requirement is very low. For instance, you can place a USD 100 order with just 3.33 US Dollar if your broker offers a 1:30 leverage ratio. However, leverage is a double-edged sword. It can amplify your losses, so heed caution when trading forex with leverage. You should avoid using high leverage.
Most Liquid Market
Forex market is also the world’s most liquid market. Liquidity refers to how quickly an asset can be sold or bought without affecting its value. Major currency pairs such as EUR/USD or USD/JPY are considered most liquid than exotic currency pairs.
Major pairs are more liquid hence the spread will be lower on major pairs. The spreads on less traded pairs are higher due to low liquidity.
Volatile
The same volatility, which makes it riskier for traders, can also present ample profit opportunities. Volatile market conditions cause rapid changes in the value of currency pairs, thus, increasing your chances of gains from the trade.
But this is also a big risk. If a currency pair changes in its value by a lot then it is considered volatile and can be a risk for investors as you can lose big if you are on the opposite side. For example, USD/TRY is considered a very volatile currency pair. You may lose quickly if you are in the wrong position, also you must consider the Swap Rates when trading such currency pairs.
Scalable
Scalable means you can trade in mini, micro, or standard lots, making it easier for traders to control investment size and capital exposure.
Affordable Technology
You don’t have to spend money on acquiring expensive hardware and software to start with forex trading. All you need is a computing device or a smartphone with a reliable internet connection. Your broker will provide charting and trading technologies at no cost once you subscribe.
Cons of Forex Trading
Following are the challenges or disadvantages of trading forex:
High Risk
Forex market is not ideal for many traders due to its high risk. The market risk in forex trading is much higher compared to other capital markets like stocks, commodities, etc. The involvement of leverage further increases the risk of losing a substantial amount within a few seconds.
The market is active 24 hours a day and any news event around the globe can affect the prices of currency pairs. Hence, at times it becomes impossible to correctly predict the price movement.
Lack of Transparency
There is no particular location from where the forex market is controlled or managed. Foreign currencies are exchanged in many ways mainly through central banks, private banks, large financial institutions, etc. The forex market is largely influenced by large-scale market makers, liquidity providers, and banks. Hence, there is no transparency about how the trade order is getting executed. The trading volume and market sentiment are also difficult to predict in the forex market.
Complex Valuation Method
The value of one currency in return for another keeps on changing due to multiple reasons at every minute. It is quite complex for retail traders to calculate the valuation of one currency in terms of another. The valuation depends on the economic and financial details of the involved currencies and their predictions. Compared to other capital markets, it is much more complex to do a valuation of the currencies.
Difficult to Learn
Stocks, commodities, and other markets are much easier to comprehend compared to the forex market. In the stock market, traders can get assistance from experts and portfolio managers. Comparatively, it is challenging to learn forex trading and understand the forex market. Traders have to learn most of the forex trading on their own.
The same volatility, which makes it riskier for traders, can also present ample profit opportunities. Volatile market conditions cause rapid changes in the value of currency pairs, thus, increasing your chances of gains from the trade.
But this is also a big risk. If a currency pair changes in its value by a lot then it is considered volatile and can be a risk for investors as you can lose big if you are on the opposite side. For example, USD/TRY is considered a very volatile currency pair. You may lose quickly if you are in the wrong position, also you must consider the Swap Rates when trading such currency pairs.
Scalable
Scalable means you can trade in mini, micro, or standard lots, making it easier for traders to control investment size and capital exposure.
Affordable Technology
You don’t have to spend money on acquiring expensive hardware and software to start with forex trading. All you need is a computing device or a smartphone with a reliable internet connection. Your broker will provide charting and trading technologies at no cost once you subscribe.
Cons of Forex Trading
Following are the challenges or disadvantages of trading forex:
High Risk
Forex market is not ideal for many traders due to its high risk. The market risk in forex trading is much higher compared to other capital markets like stocks, commodities, etc. The involvement of leverage further increases the risk of losing a substantial amount within a few seconds.
The market is active 24 hours a day and any news event around the globe can affect the prices of currency pairs. Hence, at times it becomes impossible to correctly predict the price movement.
Lack of Transparency
There is no particular location from where the forex market is controlled or managed. Foreign currencies are exchanged in many ways mainly through central banks, private banks, large financial institutions, etc. The forex market is largely influenced by large-scale market makers, liquidity providers, and banks. Hence, there is no transparency about how the trade order is getting executed. The trading volume and market sentiment are also difficult to predict in the forex market.
Complex Valuation Method
The value of one currency in return for another keeps on changing due to multiple reasons at every minute. It is quite complex for retail traders to calculate the valuation of one currency in terms of another. The valuation depends on the economic and financial details of the involved currencies and their predictions. Compared to other capital markets, it is much more complex to do a valuation of the currencies.
Difficult to Learn
Stocks, commodities, and other markets are much easier to comprehend compared to the forex market. In the stock market, traders can get assistance from experts and portfolio managers. Comparatively, it is challenging to learn forex trading and understand the forex market. Traders have to learn most of the forex trading on their own.
Chapter #8
What are the Costs of Forex Trading?
The cost that will be incurred by traders in forex trading will differ from broker to broker. Each broker charges different types of fees and the amount of fees can also be different.
Spreads and commissions are the major source of revenue for brokers and liquidity providers.
To be familiar with the fee structure, clients must check or inquire about the following components of fees before opening the account.
These are the common ways in which a forex broker will charge the traders in Australia for trading.
1) Spreads: Spreads are the major component of fees involved in forex trading. This is the difference between the bid and ask price or the buy and sell price.
Wider spreads mean lesser profit and lesser probability to make profits in a forex trade. Clients should seek brokers that offer narrower spreads.
2) Trading Commission: The commission that is incurred while executing trade orders is called a trading commission.
Some brokers offer commission-based trading on currency pairs with low spreads or zero spreads. Commission-based spread-free trading is considered ideal for large-volume traders and scalpers.
A commission on forex pairs can range from $2 to $10 for a Roundturn trade (both sides) of a Standard Lot. Details of commission (if charged) must be checked before opening the account.
3) Swap Fees: Swap fees are also called overnight charges. These are the charges that are incurred if a trading position is kept open overnight.
Orders that are opened and closed on the same day will incur no swap fees at all.
For every night the position is kept open, the swap fees will be added. Swap rates or overnight charges differ from broker to broker on every instrument.
4) Non-Trading Charges: These are the charges that will be incurred without executing trade orders. Non-trading charges can be of various types and can be tricky to identify as they are not clearly mentioned.
5) Inactivity Fee: An inactivity fee is a fee that gets deducted from the account balance if no trade orders are executed in a prolonged period of 3 months to 1 year.
6) Deposits & Withdrawals: Deposits and withdrawals can incur additional commission for some or all of the methods. Clients must check the commission or fees for deposits and withdrawals.
Other non-trading charges include account opening fees, conversion fees, internal transfer fees, etc. Subscription to additional services can also cost additionally.
Clients must enquire from the support executives about the non-trading charges separately.
Forex Trading FAQs
Is Forex Trading legal?
Forex trading is completely legal in the UK & is regulated by FCA. If you’re choosing an online broker, ensure that it is authorized by FCA. You can check the broker’s Reference No. and they verify it from FCA’s public Register. Also, verify the broker’s website before signing up.
Is forex trading profitable?
How much money is required for trading?
How can beginners learn forex trading?
Who regulates the forex market?
How long does it take to become a master of forex trading?
Can you get rich by forex trading?
How do I start forex trading for beginners?
Is $100 enough to start forex?
Is forex trading good for beginners?
Which currency pairs are most profitable?




