Forex Trading in Kenya
Forex Trading in Kenya is regulated by The CMA (Capital Markets Authority of Kenya), and there are 6 Regulated Forex Brokers in Kenya that you can safely & legally trade with. In this guide we will cover how you can start forex trading, the basics, risks & more.
Online Forex Trading in Kenya is regulated & can be done legally via authorized Forex Brokers.
The Regulatory body responsible for Regulating Online Forex Brokers in Kenya is the Capital Markets Authority (CMA). As of January 2024, there are 7 registered online forex brokers authorized by the Capital Markets Authority (CMA).
The CMA has advised Kenyan citizens who wish to trade in the foreign exchange market to do so with brokers who are authorized by the CMA. This advice is important as this would protect traders against bad business practices by illegal & offshore brokers.
5 Steps to Start Forex Trading for Beginners in Kenya
Summary Table of CMA Regulated Forex Brokers in Kenya for Traders in 2024
| Broker Name | Highlights | Trading Fees (Benchmark EUR/USD Standard Accounts) | Account Minimum | Max. Leverage | Learn More |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
FXPesa is regulated by local regulatory authoprity CMA of Kenya with license number 107. |
Commissions
1.4 pips
with Executive Account |
Account Minimum
$5
|
Max. Leverage
1:400
|
Open Account
on FXPesa |
|
|
HotForex is regulated by local regulatory authoprity CMA of Kenya with license number 155. |
Commissions
1.3 pips
with Standard Account |
Account Minimum
$5
|
Max. Leverage
1:400
|
Open Account
on HotForex |
|
|
Exinity is regulated by local regulatory authoprity CMA of Kenya with license number 135. |
Commissions
0 pips & $4/lot
with Standard Account |
Account Minimum
$20
|
Max. Leverage
1:400
|
Open Account
on Exinity |
|
|
Pepperstone is regulated by local regulatory authoprity CMA of Kenya with license number 128. |
Commissions
0.6
with Standard Account |
Account Minimum
$100
|
Max. Leverage
1:400
|
Open Account
on Pepperstone |
Chapter #1
What is Forex Market?
Forex trading is like a global market where people trade different currencies. Imagine you have two kinds of money, let’s say dollars and euros. You want to exchange some of your dollars for euros because you think the euro might become more valuable.
So, you go to this big market, and you find someone who wants to trade their euros for your dollars. You agree on a price, make the trade, and now you have euros instead of dollars. If the euro’s value goes up, you can exchange it back for more dollars and make a profit.
But it’s a bit like a game because the values of currencies keep changing all the time. So, you need to be careful and think about when to trade to make money. Forex trading is like playing with money from different countries and trying to win by trading them at the right time.
The foreign exchange market, or forex market, serves as a global platform for the exchange of currencies at prevailing rates. It facilitates international transactions by necessitating the exchange of different currencies. To ensure a fair trade, currencies are exchanged based on conversion rates, which vary for each currency pair and are influenced by a multitude of economic and geopolitical factors.
Traders engage in the forex market by analyzing these factors to predict the price movements of currency pairs. Leveraging their insights, they place buy or sell orders through margin trading. However, it’s crucial to recognize that forex trading carries a high level of risk, and many beginners face initial losses.
The forex market offers a diverse range of currency pairs, categorized as major, minor, and exotic. The EUR/USD pair is the most heavily traded globally, closely followed by GBP/USD. Trading in any currency pair signifies the exchange of one currency for another, underlining the intricate dynamics of this financial market.
The Foreign exchange market in recent times has been digitalized through technology. This has made trading go round the clock every day and five and half days per week. Currencies are traded in major financial centers across different time zones of the world from New York to London, Paris, Hong Kong, Frankfurt, Tokyo, and Zurich.
The digitalization of the forex market has also enabled individuals and retail investors to participate in the market. This is unlike as it was in the past when only large investment organizations and banks could participate in the market.
Chapter #2
What is Forex Trading?
Forex Trading is simply the exchange of one currency for another for any reason. While this definition seems easy, it leaves a lot of questions. One such question is how does Forex Trading work?
To explain how Forex works, we must know the reason people engage in Forex Trading.
If a Kenyan business wants to buy goods from the US, they will have to exchange their Kenyan shilling for USD to pay the business in the United States. This exchange is usually done through banks or other approved institutions.
However, some engage in Forex trading to hedge their risk and even make a profit. These traders try to forecast the rise and fall of currency pairs.
Forex trading is carried on through currency pairs that are, currencies are paired against each other Ex. EURUSD, CADGBP, AUDUSD, EURJPY, etc.
If a trader believes the USD will rise against the EUR, he buys USD against the EUR and sells after sometime after the price of the USD must have increased.
Another way people or mostly retail traders trade/speculate in the Forex market is through Contract for Difference (CFDs). But what are CFDs?
Contract for Difference refers to an agreement between two parties where the difference between opening and closing of trade is settled in cash. In Forex & CFD trading via an Online Forex Broker, the trader does not buy any currency, rather he/she kind of bets through the broker on the trajectory or price movement of the Forex currency pair.
One unique feature of Forex Trading in recent times is the use of margin in trades. What is margin trading?
This is a way of trading using funds provided by a third party. What this means is that the trader provides a small amount or deposit which enables him to access greater trading capital.
Margin trading allows traders to use leverage for greater potential returns on instruments traded with little amount. However, it can also lead to greater losses if the trade goes south (against your direction).
Forex & other CFD Instruments at Forex Brokers are usually traded on margin.
For example, a typical leverage offered by CMA Regulated Forex broker is around 400:1. Let’s say are trader is using 1:50 leverage, you would only require 2% as margin i.e. if the trader deposits $1000, it will be multiplied by 50, so you can trade a position size of USD 50,000.
Such margin magnifies the trading result by 50 irrespective of the trajectory of the trade.
We will now try to explain major terms associated with forex trading.
1) Currency pair: This is the listed value of one currency in relation to another in the forex market. By this, we mean to compare the value of one currency to another. It gives us an idea of how much of a currency is needed to get one unit of the other. Currencies are known by their ISO currency code which is usually three letters.
2) Pip: Also known as percentage in point, a pip is a small price movement or change in the value of a currency pair. Currency values are usually measured in four decimal places which is equal to 1/100 of 1 percent. The term spread is usually used by traders to determine the bid and ask prices between two currency pairs.
3) Lot size: This is the number of units traded in forex. What it means is that a lot is a unit of measurement that standardizes trade size. The idea behind lots is that since it is impossible to trade single units of currencies, lots provide the opportunity to trade the small changes or movements in currency prices in large tranches. There are four types of lots in forex. They are; Standard (100,000 Units), Micro (10,000 Units), Mini (1000 Units) and Nano lots. But most forex brokers only offer Micro Lots as the lowest lot size.
Chapter #3
Understanding Forex Trading with an Example
Understanding forex trading can be complex for those who have never traded on any financial instrument online in the past. Those who have a slight experience trading other capital markets like stocks, cryptocurrencies, or CFDs would be very comfortable with forex trading.
Let us understand the complete process and working methodology of the forex market with the help of an example.
Online forex trading is done through the trading platform which is software that can be downloaded on electronic devices. The trading platform connects traders to brokers, liquidity providers, and other forex traders.
Traders place buy or sell orders through trading platforms on their preferred trading instruments. The exposure and profit/loss depending on the volume traded and the leverage involved.
Leverage of 1:10 will allow you to open a position worth $100 exposure with $10 in your trading account.
In this example, we will take the leverage of 1:10 on the EUR/USD currency pair. The supposed market price for EUR/USD is 1.2100/1.2102. This means that the bid price is 1.2100 (the price that the dealer is willing to pay) and the ask price is 1.2102 (the price at which the dealer is willing to buy) and the spread is 2 pips (difference between the bid and ask price at 4th decimal).
First, we will place a buy order for 1 standard lot (100,000 units of the base currency). To place a buy order of 1 standard lot in EUR/USD, the following will be the calculation of the required account balance.
$1.2102 * 100,000 * 1/10 = $12,102
(ask price) * (units of base currency) * (leverage ratio) = (minimum account balance required to open the given position)
Now suppose the price of EUR/USD went up by 100 pips and reaches 1.2200/1.2202. By closing the buy position at this price, the following will be the profit.
(1.2200 * 100,000 * 1/10) – $12,102 = $12,200 – $12,102 = $98
(bid price * units of base currency * leverage ratio) – (exposure) = Profit/Loss
Now let us understand the same scenario with a short position on EUR/USD with 1 standard lot at the current market price of 1.2100/1.2102. Following will be the exposure amount in a short position.
$1.2100 * 100,000 * 1/10 = $12,100
(bid price) * (units of base currency) * (leverage ratio) = (minimum account balance required to open the given position)
Now suppose the price of EUR/USD went down by 150 pips and reaches 1.1950/1.1952. By closing the position at this position, the following will be the profit.
$12,100 – $(1.1952 * 100,000 * 1/10) = $12,100 – $11,952 = $148
exposure – (ask price * units of base currency * leverage ratio) = profit
It must be noted the exposure amount ($12,102 in the long position example and $12,100 in the short position example) will be at risk of capital markets. If the leverage is high, the profit/loss amount will move more with the change in the pip value of the underlying asset. Chapter #4 Forex trading is not illegal in Kenya. It is highly legal however there are rules to forex trading in Kenya. The Capital Markets Authority is the government regulator responsible for regulating forex trading in Kenya. Traders from Kenya must only trade with forex brokers who are regulated by the CMA. There are only six forex brokers regulated by the Capital Markets Authority in Kenya. These Six registered forex brokers are; FXPesa, HotForex Kenya, Scope Markets Kenya, Pepperstone Kenya, Exinity East Africa Limited & Windsor Markets (Kenya) Limited. To protect one’s funds and investment, the Capital Markets Authority has advised Kenyan citizens to verify the registration of the broker with the CMA. Most forex brokers do post their regulators on their websites. However, you need to verify the authenticity of the post on their website. We will demonstrate in simple steps how to verify a broker that is registered with the CMA. Step 2) Search the name of the broker you wish to verify on the search icon of the CMA website. In this case, we will search for FXPesa. Step 3) The search result will determine the registration status of the broker. In this case, we found results on FXPesa. Step 4) To confirm the registration status of the broker, click on any press release carrying the name of the broker. Step 5) If the broker is not registered with the CMA, the result of the search will be zero results. Exness was used to demonstrate this here. Some fake brokers can use the cloned names of the CMA-regulated brokers in Kenya. Clients must look out for spelling errors and other signs of deceitful activities. Checking the authenticity of the CMA license is very important before choosing a broker in Kenya. The steps in opening a forex account with a broker are similar across different brokerage firms in Kenya. It involves having a functional email, phone number, and perhaps a bank account. Step 1: Registration: This consists of three sections; Provision of personal details, contact details, and trading experience/employment status. This process is instant and moves from one to another. You’re expected to input correct details as they’ll be verified. You’ll be requested to put your phone number and a PIN will be sent to you to complete that stage. Step 2: Verification of accounts: Here you’ll have to upload a passport and valid means of identification, most likely a government identity card. In this stage, a text message will be sent to you with a link to start the verification/activation of the account. On clicking the link, you’ll be asked to provide your password and start the verification process. Step 3: Confirmation of documents submitted by you: This process is not instant as the rest are. On confirmation of the documents submitted, you’ll be able to make deposits and start trading. Before rushing in to open a forex trading account, clients must comprehend the components of fees that can be incurred from them while trading forex and CFDs online. Each broker can charge differently for trading forex. The following components of fees must be checked and compared before choosing a forex broker in Kenya. Trading fees include all the fees that are incurred while executing trade orders. Spread: Spread is the most important fee that a trader has to pay while trading forex or any other CFD instrument. It is the difference between the bid and ask price of an instrument. Wider spreads mean higher revenues for the broker and lesser gains for the traders. Trading Commission: Some brokers may incur a fixed or variable commission (depending on the trading volume). Spreads may or may not be incurred while trading with commissions. Most brokers offer a separate account type for commission based trading at low spreads. This commission is incurred while opening as well as closing the position depending on trading volume. Overnight Charges: Overnight charges are also called as swap fee or rollover charges. This is the fee that is incurred when a leveraged position is kept open overnight. Each instrument has different overnight charges for long as well as short position. Traders who prefer to keep their positions open for more than a week must check swap fees before doing so. These are the charges that are incurred without executing trade orders. Inactivity Fees: Most brokers charge inactivity fees if no trades are executed for a prolonged period after opening the account. The inactivity period and the monthly charges for inactivity can be different for each broker. Some brokers charge inactivity fees after 3 months of inactivity some for 12 months while many do not charge any inactivity fees. Deposit/Withdrawal Fees: As the name suggests, this fee will be incurred for each deposit or withdrawal. each Deposit and withdrawal method can have a different fee associated with a broker. Clients must check and compare the transaction fees for their preferred mode of deposit and withdrawal. Currency Conversion Fees: These are the fees that are only incurred if the deposit currency is different from the base currency of the account. Most brokers use nominal currency exchange rates but each broker can have different currency conversion charges. Account Opening/Maintenance Fees: Account opening is free at all the CMA-regulated brokers in Kenya. However, some other forex and CFD brokers do charge account opening or regular maintenance charges. The details of all the trading and non-trading fees can be checked on the official websites of the broker. Clients can also inquire about the fees through customer support services. The following are the important factors that must be considered while selecting the best forex broker for oneself in Kenya: 1. Regulations: Capital Markets Authority (CMA) is the financial regulator in the jurisdiction of Kenya. Clients getting registered under CMA regulation are protected and are exposed to less third-party risk. Traders must ensure that the chosen forex CFD broker must be regulated by CMA in Kenya. The details of the regulation are generally mentioned in the footnote of the official websites of the brokers. Clients can also access the CMA website to cross-check the regulation details of a particular broker. Currently, there are 7 forex brokers that are licensed and regulated by CMA in Kenya. 2. Fees: The spreads, commission, overnight charges, inactivity fee, deposit/withdrawal fee, and all other components of fees must be checked and compared. The higher fee is beneficial for the brokers and costly for the traders. Lower spreads can have a major impact on profits and losses booked by the trader. 3. Available Instruments: The chosen forex broker must offer adequate varieties of financial instruments including the ones that you wish to trade with. Traders must ensure that their preferred trading instrument is available with the chosen broker or not. Contract specifications on preferred instruments should also be checked before opening the account. Not every broker offers the same instruments although there are some instruments which will be offered by every forex broker. For example, the EUR/USD is offered by every forex broker. In contrast, there are some instruments which will only be offered by a few brokers. For example, not every broker offers cryptocurrencies and even if they do, the selection may be limited to Bitcoin and Ethereum. 4. Trading Platform: All trading activity will take place on the trading platform. Clients must be convenient with the trading platform and all its features. Efficient and convenient use of the trading platform will enhance the outcomes of trades. 5. Deposit/Withdrawal: The best forex broker in South Africa must accept your preferred mode of deposit and withdrawal in time without additional commission. Traders must check the processing time of deposits and withdrawals along with the fees associated with each method before opening their accounts. 6. Customer Support: The best forex broker must offer quality customer support services through live chat, email, phone, or social media applications. Easy connectivity with the support staff will enhance the trading experience as traders can resolve any query faced while trading. 7. Trading Conditions: Clients must check every trading condition like leverage, account currency, deposit currency, account types, bonus, etc to choose the best forex broker for themselves. For example, if a broker does not support KES as the base currency of the account then the deposits made in KES will be converted to base account currency at prevailing rates. For retail traders, it can be difficult to consider every aspect of a broker while choosing them. The best practice for beginners is to start with a demo account and trade with virtual currency. This will not only allow you to comprehend the trading conditions and experience with a broker but will also grant you experience to make better trading decisions. Chapter #5 It is no mean feat to trade and make a profit in the forex market as a retail trader. The market is highly volatile and only those with vast knowledge of market trends are able to trade unscathed. However, there are strategies for trading. A trader does not just open a trade without a background strategy in place. In Forex Trading, there are two strategies for analyzing the market. We have the Fundamental analysis and Technical analysis. This strategy of forex trading tries to measure the real value of a nation’s currency by assessing the factors that determine the health of a country’s economy. These factors include international trade, GDP, manufacturing, interest rate, employment rate, politics, and everyday national events. These factors are used to determine the real value of the particular currency and project future movements in price. These factors have proved relevant in determining the movement in the price of forex instruments in the past and in recent times. For example, on June 24, 2016, a day after the United Kingdom voted to leave the European Union, the Sterling plunged to a thirty-year low. Announcements of increases or reductions in interest rates by Central banks also the movement of the prices of currencies in the market. The idea behind fundamental analysis is that most times, the price of a forex instrument is usually over over-valued or under-valued. And the only way to determine its true value is to assess the various factors that determine the state of a country’s economy. Fundamental analysis as a trading strategy is best suited for long-term trades. This is true since the trader should be patient enough to sit out any rally or deep and rely on the information from his indicators. Technical analysis as a forex strategy involves analyzing symbols, patterns, and charts. Unlike fundamental analysis, a trader using technical analysis as a strategy is not concerned about the causes of the price movement. Technical analysis is not also concerned with the true value of the currency but uses charts as indicators to determine future price movement. Technical analysis traders rely on price action, trends, support, and resistance level seen on the chart. Many believe technical analysis is easier to use than the two trading forex strategies. Technical analysis is best suited for short-term trading. Both fundamental analysis and technical analysis offer credible insight into how to enter or exit a trade. It is difficult to state clearly which is better or more preferable, as it depends on the trader. We will advise traders to choose the strategy that suits them or combine both strategies in their trading. Chapter #6 Forex trading is a risky venture. There are so many risks involved in forex trading. The major risk associated with brokers is being Unlicensed in Kenya. However, most of these unlicensed brokerage firms are owned by foreigners who can easily pull out of Kenya & run away after scamming traders. For brokers that are regulated with CMA, there is capital protection & the activities of these brokers are monitored by CMA. In the event of the financial insolvency of such brokers or bad practice, there is a higher chance of protection with a regulated broker. Other risks are:
Leverage as explained earlier is the opportunity to trade with funds larger than the trader’s deposit. What this means is that, the forex broker kind of provides a margin to the trader to increase potential profit or returns. Leverage is expressed in a ratio. That is, it is the ratio of the trader’s fund to the amount of the broker’s credit. The good side about leverage is that it can easily magnify a trader’s profit. For example, if a trader uses $100 to buy the USD against the EUR with a leverage of 1:100. A 10 percent rise in the value of the USD will result in a $100 profit for the trader. However, leverage in forex has been described as a double-edged sword. While it can increase a trader’s return, it can easily wipe off a trader’s capital. For example, if a trader uses $100 to trade the EURUSD pair with a leverage of 1:100. According to his leverage, the trader can open a position worth $10,000. If he opens the EURUSD long trade at 1.1450 and closes the long position at 1.1350, he has lost his capital of $10,000 due to a leverage of 1:100. This is the danger of leverage; small price movement produces a great impact in terms of profit and losses. It is a known fact that most of the retail traders using leverage lose, hence it is important to limit your leverage to a max. of 1:20 only while trading forex, and much lower in the case of other CFD instruments. Whether you use fundamental analysis or technical analysis as a forex trading strategy, the truth is that it is difficult to anticipate the trajectory of forex price movement. This is so because the factors responsible for the price movement are complex and multi-faceted. For example, a shocking unanticipated political scandal can have a huge effect on price movement or even a natural disaster can have ripple effects on the forex market as it happened during the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. It is near impossible to predict such events, and it can bring huge losses for a trader. There are tons of forex brokers & unregulated schemes promising unrealistic returns on the internet. Many of these businesses are not registered in Kenya nor are they licensed by the CMA. As a forex trader, you must avoid such unregistered and unlicensed brokers/dealers, or schemes promoting high returns. Only a highly-skilled forex trader can be able to meander the ropes of the forex market. This is because some currency pairs in the forex market are highly volatile. Price movements can change in a flash, and go down a few points against you very quickly. This is a risk a trader has to consider when deciding to start forex trading. There are multiple risk elements in the forex market. Choosing the right broker, taking informed decisions, technical and fundamental analysis, and other precautionary measures will reduce the risk factor. However, risk in the forex market can be mitigated but cannot be removed completely. Leveraged forex trading involves significant financial risk. Forex trading is easily accessible for retail traders. More than 70% of forex traders face losses. It is always advisable to use the demo account and trade with virtual currencies before trading with real money. This will also allow traders to know whether forex trading is suitable for them or not. To mitigate these risks, forex traders should: Risk management techniques in forex trading Position Size: Determine trade size based on account balance and risk tolerance (1-2% per trade). Stop-Loss: Set stop-loss orders to limit losses if the market moves against you. Take-Profit: Use take-profit orders to secure gains at a predefined level. Risk-Reward Ratio: Aim for favorable risk-reward ratios (1:2 or better). Diversification: Spread risk by trading different assets, not all in one. Control Leverage: Use leverage carefully to align with risk tolerance. Trading Plan: Develop a clear plan with entry/exit rules and risk limits. Emotions: Manage emotions to avoid impulsive decisions. Stay Informed: Be aware of market events that could impact trades. Monitor Trades: Adjust stop-loss and take-profit levels as needed. Review Trades: Analyze trades to learn and improve strategies. Avoid Revenge Trading: Don’t trade impulsively to recover losses. Forex trading can be rewarding, but it is crucial to approach it with a clear understanding of the risks involved and to trade responsibly. Traders should consider seeking advice from financial professionals and only trade with money they can afford to lose. Chapter #7 There are some pros for traders trading in the forex market over other financial markets. But you must understand all the risks before making a decision whether to trade forex & CFDs or not.. Following are the advantages of trading forex: You invest in the world’s largest financial market. With daily transactions crossing over USD 5 trillion, the sheer size of the forex market makes it truly a global marketplace with several profit opportunities. The forex market operates around the clock so that you will find a trading opportunity any time of the day in at least one global time zone. As the forex market is a decentralized OTC market, its working hours are not subject to any centralized exchange system. For instance, trading hours begin at 5 PM EST in the USA on Sunday and roll continuously with other markets until Friday at 5 PM. Note that even though currency trading is restricted for retail traders on weekends, the exchange rate keeps moving. In addition to very low investment requirements, even the transaction cost of trading forex is relatively lower. For instance, you can start dealing in currencies with just USD 100 or even lower. The main earning of a broker comes from the bid-ask spread. Spread is measured in pips, the difference between the sell and buy price of a currency. However, some brokers do charge a commission or flat fees per transaction. You should factor in commission and spread while choosing a broker to lower your overall trading cost. The availability of high leverage is perhaps the main reason why forex trading appeals to so many people. It enables you to place a higher trading order with minimum capital. Almost all the forex brokers offer leverage where you can borrow against deposited money in your trading account. It’s similar to taking a mortgage against your property; the only difference is that the margin requirement is very low. For instance, you can place a USD 100 order with just 3.33 US dollars if your broker offers a 1:30 leverage ratio. However, leverage is a double-edged sword. It can amplify your losses, so heed caution when trading forex with leverage. You should avoid using high leverage. Forex market is also the world’s most liquid market. Liquidity refers to how quickly an asset can be sold or bought without affecting its value. Major currency pairs such as EUR/USD or USD/JPY are considered most liquid than exotic currency pairs. Major pairs are more liquid hence the spread will be lower on major pairs. The spreads on less traded pairs are higher due to low liquidity. The same volatility, which makes it riskier for traders, can also present ample profit opportunities. Volatile market conditions cause rapid changes in the value of currency pairs, thus, increasing your chances of gains from the trade. But this is also a big risk. If a currency pair changes in its value by a lot then it is considered volatile and can be a risk for investors as you can lose big if you are on the opposite side. For example, USD/TRY is considered a very volatile currency pair. You may lose quickly if you are in the wrong position, also you must consider the Swap Rates when trading such currency pairs. Scalable means you can trade in mini, micro, or standard lots, making it easier for traders to control investment size and capital exposure. You don’t have to spend money on acquiring expensive hardware and software to start with forex trading. All you need is a computing device or a smartphone with a reliable internet connection. Your broker will provide charting and trading technologies at no cost once you subscribe. Following are the challenges or disadvantages of trading forex: Forex market is not ideal for many traders due to its high risk. The market risk in forex trading is much higher compared to other capital markets like stocks, commodities, etc. The involvement of leverage further increases the risk of losing a substantial amount within a few seconds. The market is active 24 hours a day and any news event around the globe can affect the prices of currency pairs. Hence, at times it becomes impossible to correctly predict the price movement. There is no particular location from where the forex market is controlled or managed. Foreign currencies are exchanged in many ways mainly through central banks, private banks, large financial institutions, etc. The forex market is largely influenced by large-scale market makers, liquidity providers, and banks. Hence, there is no transparency about how the trade order is getting executed. The trading volume and market sentiment are also difficult to predict in the forex market. The value of one currency in return for another keeps on changing due to multiple reasons at every minute. It is quite complex for retail traders to calculate the valuation of one currency in terms of another. The valuation depends on the economic and financial details of the involved currencies and their predictions. Compared to other capital markets, it is much more complex to do a valuation of the currencies. Stocks, commodities, and other markets are much easier to comprehend compared to the forex market. In the stock market, traders can get assistance from experts and portfolio managers. Comparatively, it is challenging to learn forex trading and understand the forex market. Traders have to learn most of the forex trading on their own. Chapter #8 The cost that will be incurred by traders in forex trading will differ from broker to broker. Each broker charges different types of fees and the amount of fees can also be different. Spreads and commissions are the major source of revenue for brokers and liquidity providers. To be familiar with the fee structure, clients must check or inquire about the following components of fees before opening the account. These are the common ways in which a forex broker will charge the traders in Australia for trading. 1) Spreads: Spreads are the major component of fees involved in forex trading. This is the difference between the bid and ask price or the buy and sell price. Wider spreads mean lesser profit and lesser probability to make profits in a forex trade. Clients should seek brokers that offer narrower spreads. 2) Trading Commission: The commission that is incurred while executing trade orders is called a trading commission. Some brokers offer commission-based trading on currency pairs with low spreads or zero spreads. Commission-based spread-free trading is considered ideal for large-volume traders and scalpers. A commission on forex pairs can range from $2 to $10 for a Roundturn trade (both sides) of a Standard Lot. Details of commission (if charged) must be checked before opening the account. 3) Swap Fees: Swap fees are also called overnight charges. These are the charges that are incurred if a trading position is kept open overnight. Orders that are opened and closed on the same day will incur no swap fees at all. 4) Non-Trading Charges: These are the charges that will be incurred without executing trade orders. Non-trading charges can be of various types and can be tricky to identify as they are not clearly mentioned. 5) Inactivity Fee: An inactivity fee is a fee that gets deducted from the account balance if no trade orders are executed in a prolonged period of 3 months to 1 year. 6) Deposits & Withdrawals: Deposits and withdrawals can incur additional commission for some or all of the methods. Clients must check the commission or fees for deposits and withdrawals. Other non-trading charges include account opening fees, conversion fees, internal transfer fees, etc. Subscription to additional services can also cost additionally. Clients must enquire from the support executives about the non-trading charges separately.
How to Trade Forex in Kenya?
How to verify a broker’s registration with CMA
Step 1) Visit the official website of the CMA on www.cma.or.ke
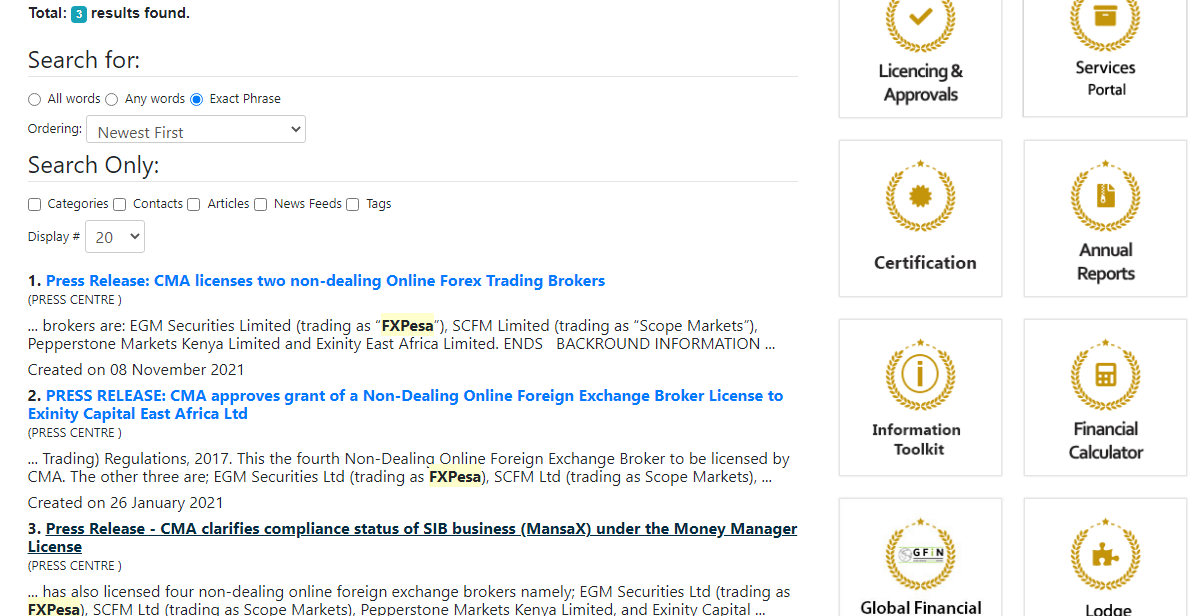
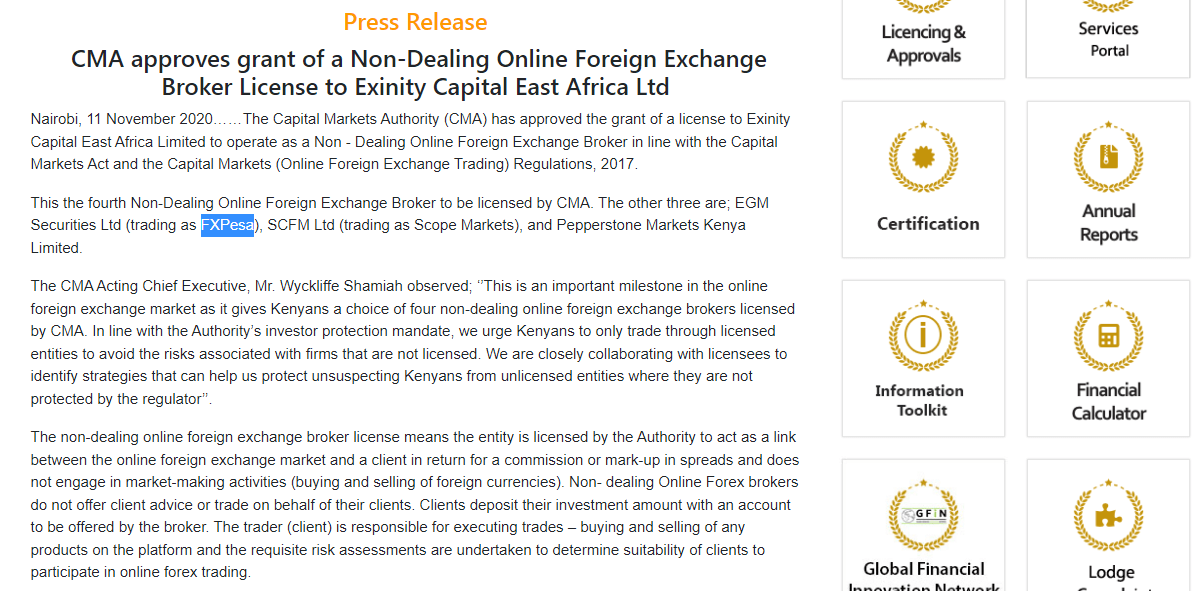
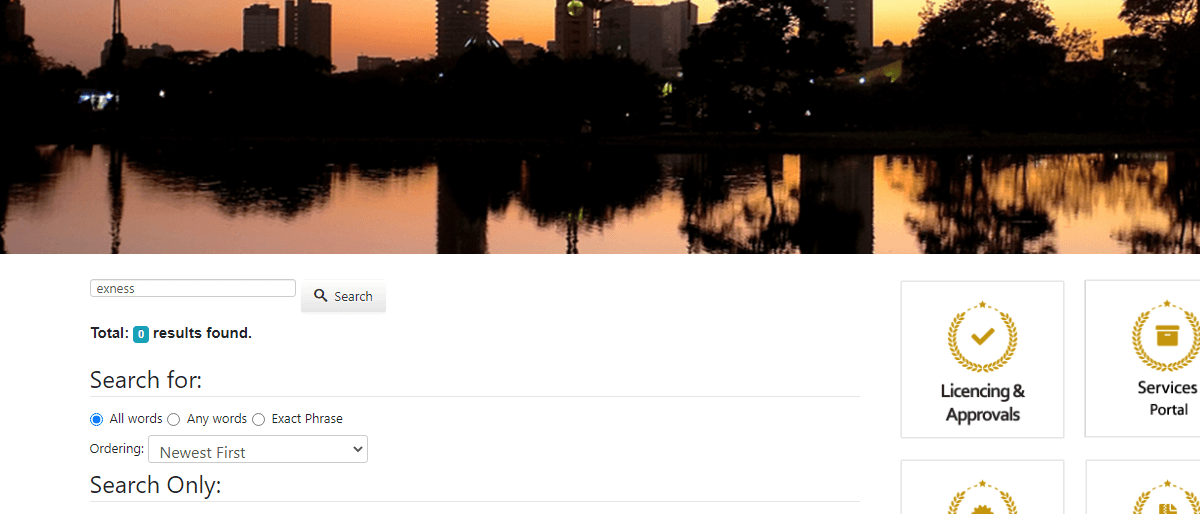
How To Open a Forex Account in Kenya?
In this guide, we will use FXPesa to describe the steps in opening an account with a forex broker in Kenya.
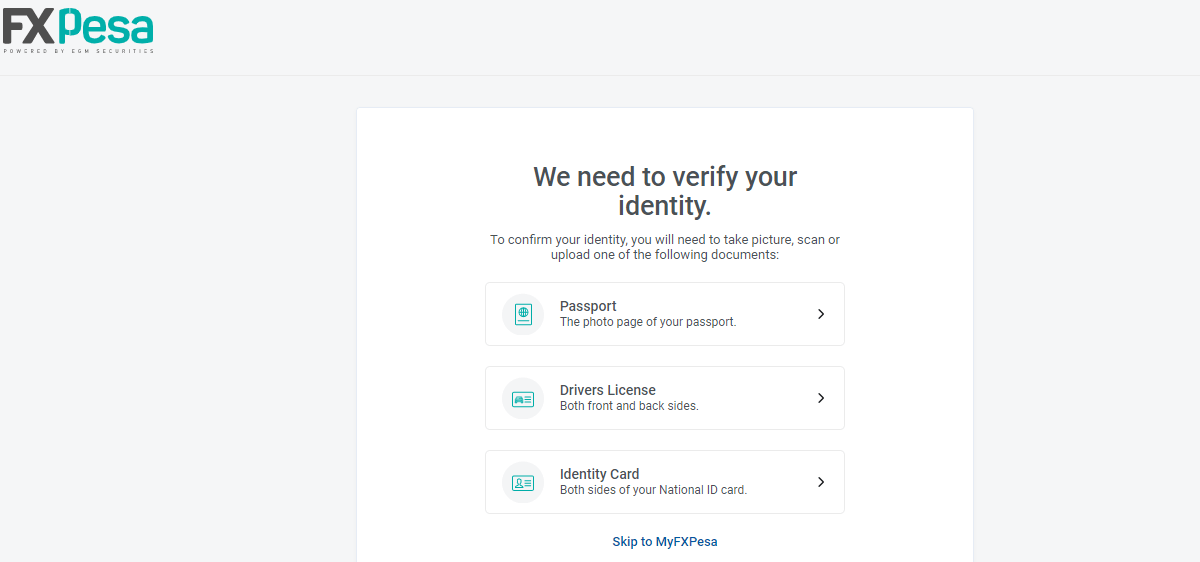
There are three steps to opening an account on FXPesa. 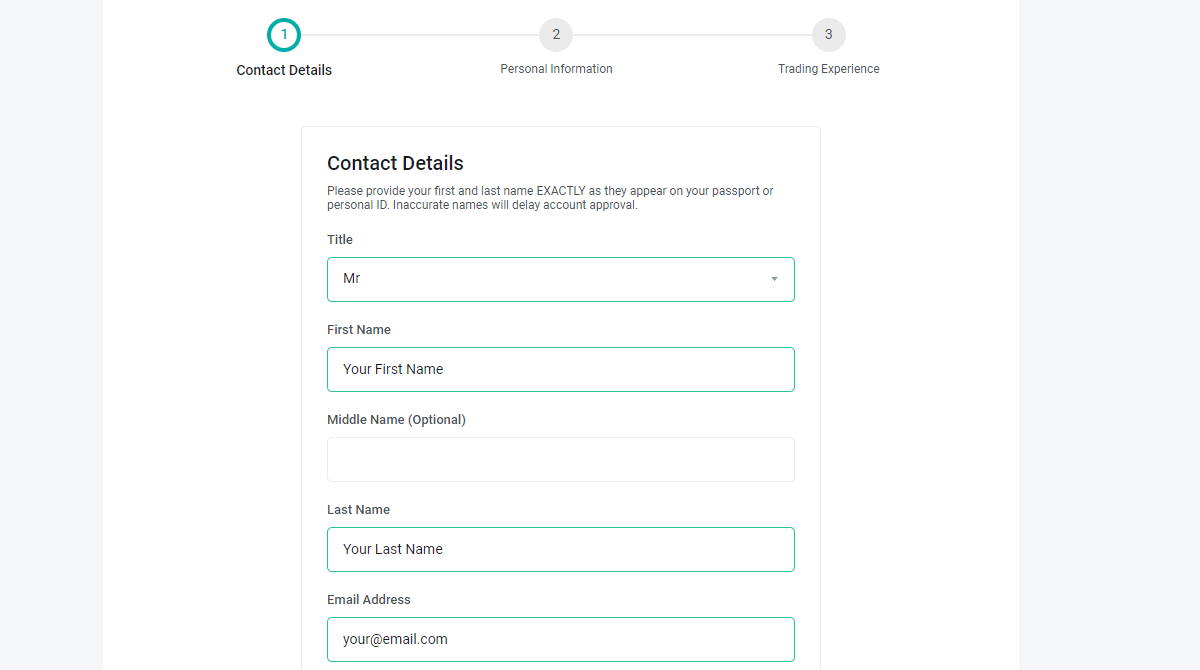
Fees Involved in Forex Trading
Trading Fees
Non-Trading Fees
How to Choose a Forex Broker in Kenya
Forex Trading Strategies
Fundamental Analysis
Technical Analysis
Risks in Forex Trading
1) Risk of Using Leverage
2) Difficulty in Predicting Currency Movements
3) Scams
4) Volatility Risk
Pros and Cons of Forex Trading
Pros of Forex Trading
Largest Capital Market
24-Hour Market
Low Capital Requirement and Lower Transaction cost
Availability of Leverage
Most Liquid Market
Volatile Market
Scalable
Affordable Technology
Cons of Forex Trading
High Risk
Lack of Transparency
Complex Valuation Method
Difficult to Learn
What are the Costs of Forex Trading?
For every night the position is kept open, the swap fees will be added. Swap rates or overnight charges differ from broker to broker on every instrument.
Forex Trading FAQs
Is forex trading legal in Kenya?
Forex trading is legal in Kenya but you must trade with a broker licensed by the Kenyan Capital Markets Authority. Currently, only 6 forex brokers with no dealing desk are regulated by CMA. However, more than 20 forex brokers with offshore regulations accept clients from Kenya.
How do I start trading forex?
What is forex trading and how it works?
Can Forex make you a millionaire?
Is forex trading profitable?




